The Uniform Juvenile Court Act Provides That A Delinquent Cannot Be Detained In A
The JJDP Act of 2002 provides that juveniles alleged to be or found to be delinquent as well as status offenders and non-offenders will not be detained or confined in any institution in which they have contact with adult inmates. Committed a delinquent act before reaching eighteen years of age or who is alleged to.
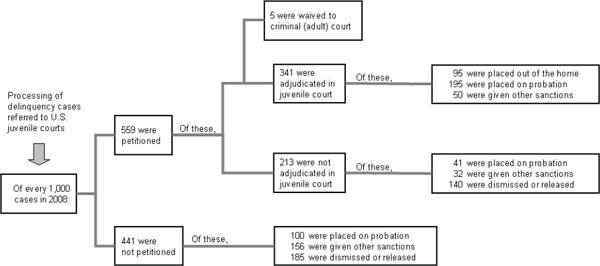 3 Current Practice In The Juvenile Justice System Reforming Juvenile Justice A Developmental Approach The National Academies Press
3 Current Practice In The Juvenile Justice System Reforming Juvenile Justice A Developmental Approach The National Academies Press
Juvenile delinquency rather than a legalistic one were attached to most urban juvenile courts.
The uniform juvenile court act provides that a delinquent cannot be detained in a. If the court finds that a child who has been adjudged to have committed a delinquent act or to be unruly or deprived is or is about to become a resident of another state which has adopted the Uniform Juvenile Court Act or a substantially similar Act which includes provisions corresponding to sections 27-20-39 and 27-20-40 the court may defer hearing on need for treatment or rehabilitation. 4 older who is excluded from the jurisdiction of the juvenile 5 court pursuant to section 2328 subsection 1 paragraph c 6 while awaiting trial or other legal process shall not be 7 detained in any facility intended for the detention of adults 8 unless the court determines that after a hearing and issuing. Juvenile courts viewed the juvenile offender not as a criminal but as an errant youth and sought to rehabilitate rather than to punish2 The Second Phase The next phase smphasized both the need to make changes in the older.
Provided that if at any time afterwards it appears to the Juvenile Court on receiving a report from the probation officer or otherwise that the delinquent juvenile has not been of good behavior during the period of supervision or that the fit institution under whose care the juvenile was placed is no longer able or willing to ensure the good behavior and well-being of the juvenile it may. In 1974 when Congress first enacted the Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention Act more than 640000 youth were admitted to juvenile detention or corrections facilities and the daily population of youth in confinement was 79000. Non-offender means a detained juvenile other than one charged with an act of delinquency or a status offense.
These are cases involving minors whose actions if they were adults would be considered crimes and would result in a case in criminal court. Dependency actions are cases in which a child has been alleged to have been abandoned neglected or abused. It is the prosecutor who decides whether or not a juvenile will be adjudicated delinquent.
13 Back then an estimated 20 of all boys in juvenile facilities and 70 of all girls were confined for status offenses not delinquency. RULES OF JUVENILE COURT PROCEDURE DELINQUENCY MATTERS PART D MASTERSJUVENILE COURT HEARING OFFICERS. Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention.
Juvenile Court handles delinquency actions dependency actions and Marchman Act petition cases involving children under 18 years old. The court will provide you with a copy of the complaint a legal court. Uniform Rules of the Family Court 22 NYCRR.
Delinquent Offenders Funding provided by the Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention pursuant to Title II of the Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention JJDP Act of 2002 as revised. History of the JJDPA. Research continues to show that most youth who are detained in juvenile detention centers have been exposed to both community and family violence and many have been threatened with.
Subsequent juvenile court involvement have faced both serious adversities and trau - matic experiences. An Act to provide a comprehensive coordinated approach to the problems of juvenile delinquency and for other purposes. Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention Act of 1974.
If your child is not detained after the initial detention hearing another. JJDP Act means the Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention Act of 2002 PL. Juvenile punishment and the procedures used in juvenile delinquency courtrooms differs significantly from adult criminal courts.
August 2020 Custody of Status vs. Delinquency is defined as an act by a juvenile under the age of 18 that if committed by an adult would constitute a crime. Established in 1974 and most recently authorized in 2018 with bipartisan support the Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention Act JJDPA is based on a broad consensus that children youth and families involved with the juvenile and criminal courts should be guarded by federal standards for care and custody while also upholding the interests of community safety and.
Delinquency actions are cases in which a child is alleged to have committed a law violation. 5601 et seq and regulations thereunder 28 CFR31303. If a juvenile is detained the juvenile shall be brought before the judge who issued the warrant a judge or.
Prevent and control juvenile delinquency and improve the juvenile justice system. Delinquent act means an act designated a crime under the law including local ordinances or resolutions of this state or of another state if the act occurred in that state or under federal law and the crime does not fall under subdivision c of subsection 21. For additional copies contact the Juvenile Justice Compliance Monitor at.
According to the Uniform Juvenile Court Act aan blank. Juvenile means an individual who is under the age of 18 years. The 93rd United States Congress.
According to the Uniform Juvenile Court Act aan _____ child cannot be placed in a correctional institution unless after additional investigation the court finds the child is nor amendable to treatment or rehabilitation under a previous non-correctional disposition. Unruly children dependency or neglect provided that the respondent is within the age range and geographical area specified by the court. Given by order of a court.
Family Court Act 3555 requires a permanency hearing regarding juveniles who are placed in non-secure facilities although all juveniles placed pursuant to Family Court Act 3533 are subject to extensions of placement.
 Juvenile Justice Test 1 Test 2 And Final Cumulative Flashcards Quizlet20benchbook Chapter 203 20overview 20of 20pennsylvania 27s 20juvenile 20justice 20system Pdf
Juvenile Justice Test 1 Test 2 And Final Cumulative Flashcards Quizlet20benchbook Chapter 203 20overview 20of 20pennsylvania 27s 20juvenile 20justice 20system Pdf
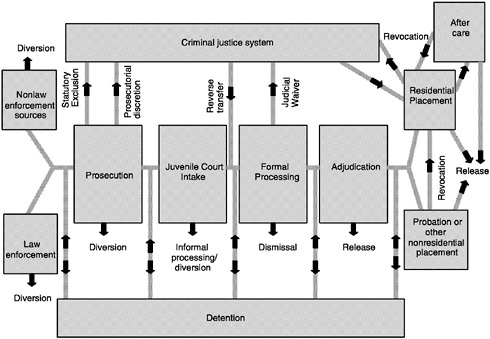 The Juvenile Justice System Juvenile Crime Juvenile Justice The National Academies Press
The Juvenile Justice System Juvenile Crime Juvenile Justice The National Academies Press
Posting Komentar untuk "The Uniform Juvenile Court Act Provides That A Delinquent Cannot Be Detained In A"